
Double declining balance depreciation allows for higher depreciation expenses in early years and lower expenses as an asset nears the end of its life. The Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits Method also falls into the category of accelerated depreciation methods. It involves more complex calculations but is more accurate than the Double Declining Balance Method in representing an asset’s wear and tear pattern. This method balances between the Double Declining Balance and Straight-Line methods and may be preferred for certain assets.
Pros of the Double Declining Balance Method
However, the management teams of public companies tend to be Insurance Accounting short-term oriented due to the requirement to report quarterly earnings (10-Q) and uphold their company’s share price. Since public companies are incentivized to increase shareholder value (and thus, their share price), it is often in their best interests to recognize depreciation more gradually using the straight-line method. In many countries, the Double Declining Balance Method is accepted for tax purposes. However, it is crucial to note that tax regulations can vary from one jurisdiction to another.

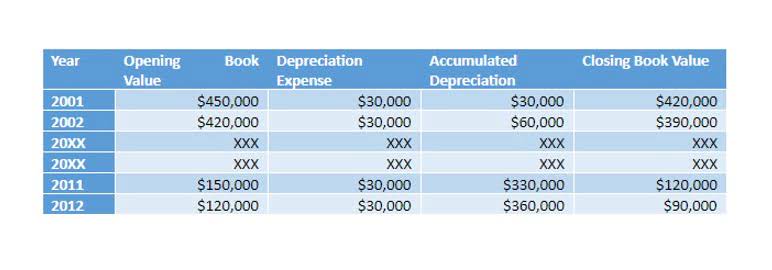
Annual Depreciation Expense Calculation (DDB)
- Sara wants to know the amounts of depreciation expense and asset value she needs to show in her financial statements prepared on 31 December each year if the double-declining method is used.
- And the book value at the end of the second year would be $3,600 ($6,000 – $2,400).
- By front-loading depreciation expenses, it offers the advantage of aligning with the actual wear and tear pattern of assets.
- Our mission is to equip business owners with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions.
- For example, if an asset has a useful life of 10 years (i.e., Straight-line rate of 10%), the depreciation rate of 20% would be charged on its carrying value.
- When the depreciation rate for the declining balance method is set as a multiple, doubling the straight-line rate, the declining balance method is effectively the double-declining balance method.
In case of any confusion, you can refer to the step by step explanation of the process below. The final step before our depreciation schedule under the double declining balance method is complete is to subtract our ending balance from the beginning balance to determine the final period depreciation expense. The double declining balance (DDB) depreciation method is cash flow an accounting approach that involves depreciating certain assets at twice the rate outlined under straight-line depreciation. This results in depreciation being the highest in the first year of ownership and declining over time.
How do I record depreciation using the Double Declining Balance Method in my financial statements?
In that year, the depreciation amount will be the difference between the asset’s book value at the beginning of the year and its final salvage value (usually a small remainder). In contrast to straight-line depreciation, DDB depreciation is highest in the first year and then decreases over subsequent years. This makes it ideal for assets that double declining balance method typically lose the most value during the first years of ownership. Let’s assume that FitBuilders, a fictitious construction company, purchased a fixed asset worth $12,500 on Jan. 1, 2022.

Download our Sample Ecommerce Financial Reports
- This method falls under the category of accelerated depreciation methods, which means that it front-loads the depreciation expenses, allowing for a larger deduction in the earlier years of an asset’s life.
- Instead of multiplying by our fixed rate, we’ll link the end-of-period balance in Year 5 to our salvage value assumption.
- DDB is ideal for an asset that very rapidly loses its value or quickly becomes obsolete.
- The final step before our depreciation schedule under the double declining balance method is complete is to subtract our ending balance from the beginning balance to determine the final period depreciation expense.
- Even if the double declining method could be more appropriate for a company, i.e. its fixed assets drop off in value drastically over time, the straight-line depreciation method is far more prevalent in practice.
- In addition, capital expenditures (Capex) consist of not only the new purchase of equipment but also the maintenance of the equipment.
- An exception to this rule is when an asset is disposed before its final year of its useful life, i.e. in one of its middle years.
Accountingo.org aims to provide the best accounting and finance education for students, professionals, teachers, and business owners. In addition, capital expenditures (Capex) consist of not only the new purchase of equipment but also the maintenance of the equipment. And the book value at the end of the second year would be $3,600 ($6,000 – $2,400). This cycle continues until the book value reaches its estimated salvage value or zero, at which point no further depreciation is recorded. The beginning of period (BoP) book value of the PP&E for Year 1 is linked to our purchase cost cell, i.e.
